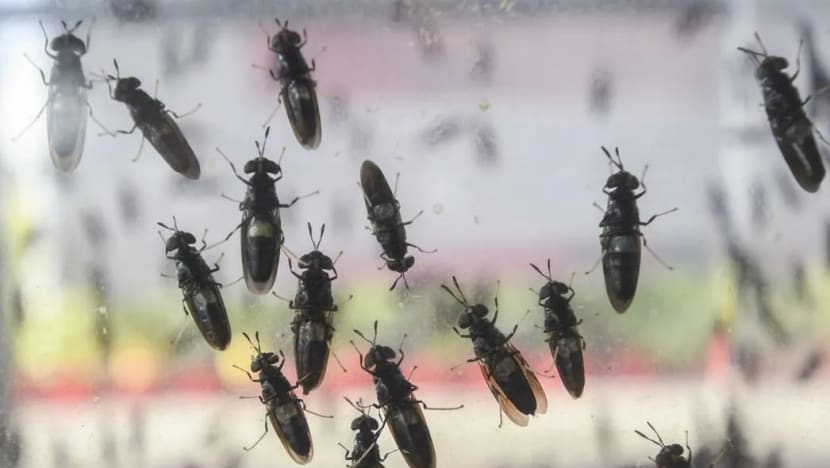
Have you ever heard of the black soldier fly? This little insect may hold the key to revolutionizing the way we view protein sources in the future. With its high protein content and efficient farming methods, the black soldier fly has the potential to significantly impact the global food industry. Not only is it a sustainable option, but it also has numerous environmental benefits compared to traditional livestock farming. In this blog post, we will delve into the potential of the black soldier fly as a protein source, exploring its benefits and potential drawbacks.
=> Quick Answer: YES! Absolutely, the Black Soldier Fly Larvae has the potential to be the protein of the future. Its sustainability, nutritional benefits, and versatility make it a compelling candidate for addressing global food challenges and reducing the environmental footprint.
The Black Soldier Fly?
Your interest in the black soldier fly as a potential source of protein for the future is well-founded. This remarkable insect possesses numerous unique qualities that make it a promising candidate for sustainable protein production. Understanding the biology, lifecycle, and nutritional profile of the black soldier fly is crucial in evaluating its potential as a protein source.
Biology and Lifecycle of the Black Soldier Fly
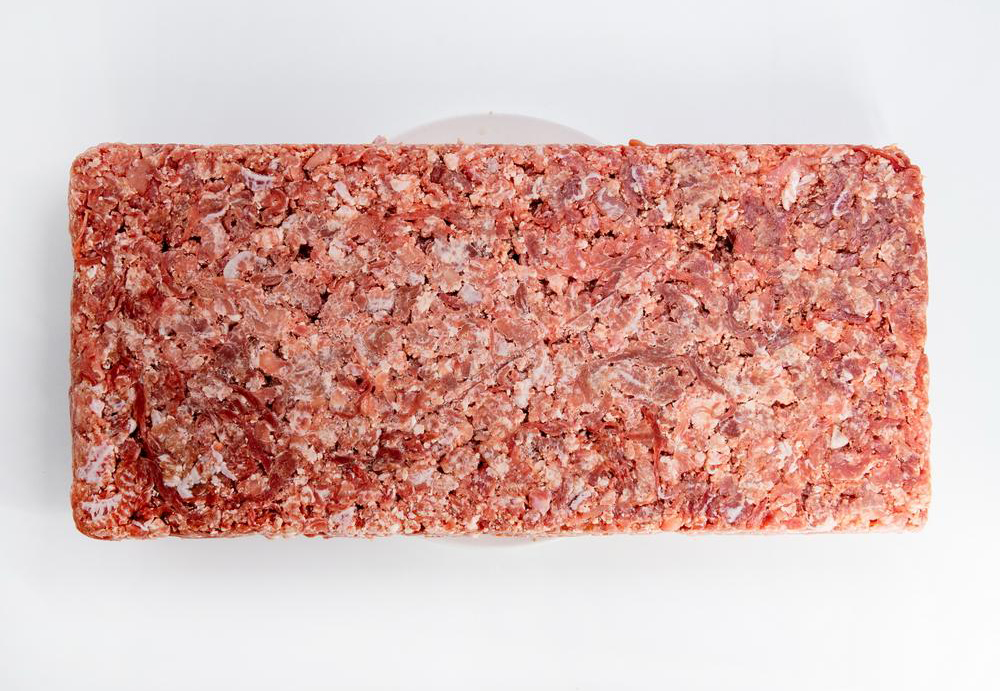
The black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) is a non-pest, beneficial insect that plays a vital role in organic waste management. Unlike other fly species, black soldier flies do not have mouthparts designed for biting or stinging, making them harmless and non-invasive. The lifecycle of a black soldier fly consists of four main stages: egg, larva, prepupa, and adult. The larvae, in particular, are voracious eaters and can consume a wide range of organic waste materials, including kitchen scraps, livestock manure, and even sewage. Their ability to efficiently convert organic waste into valuable biomass is one of the key factors that make them a promising protein source.
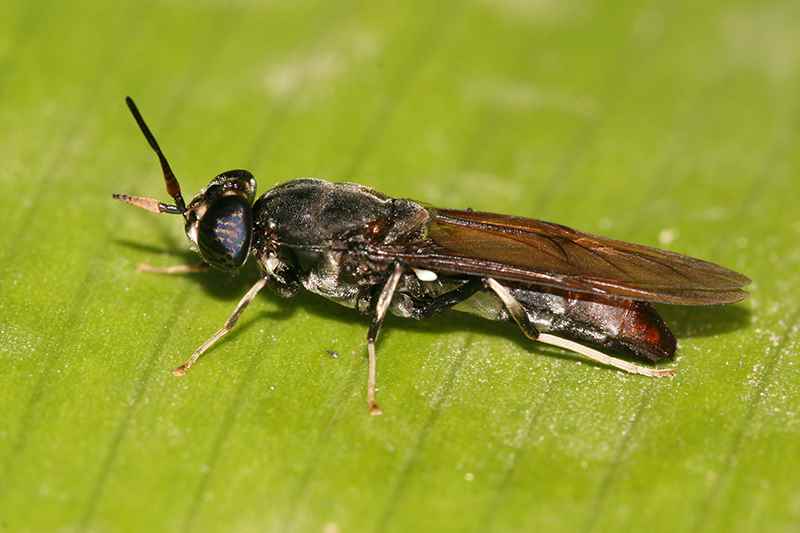

Black soldier fly is a type of fly originating from Europe that is very common in the wild
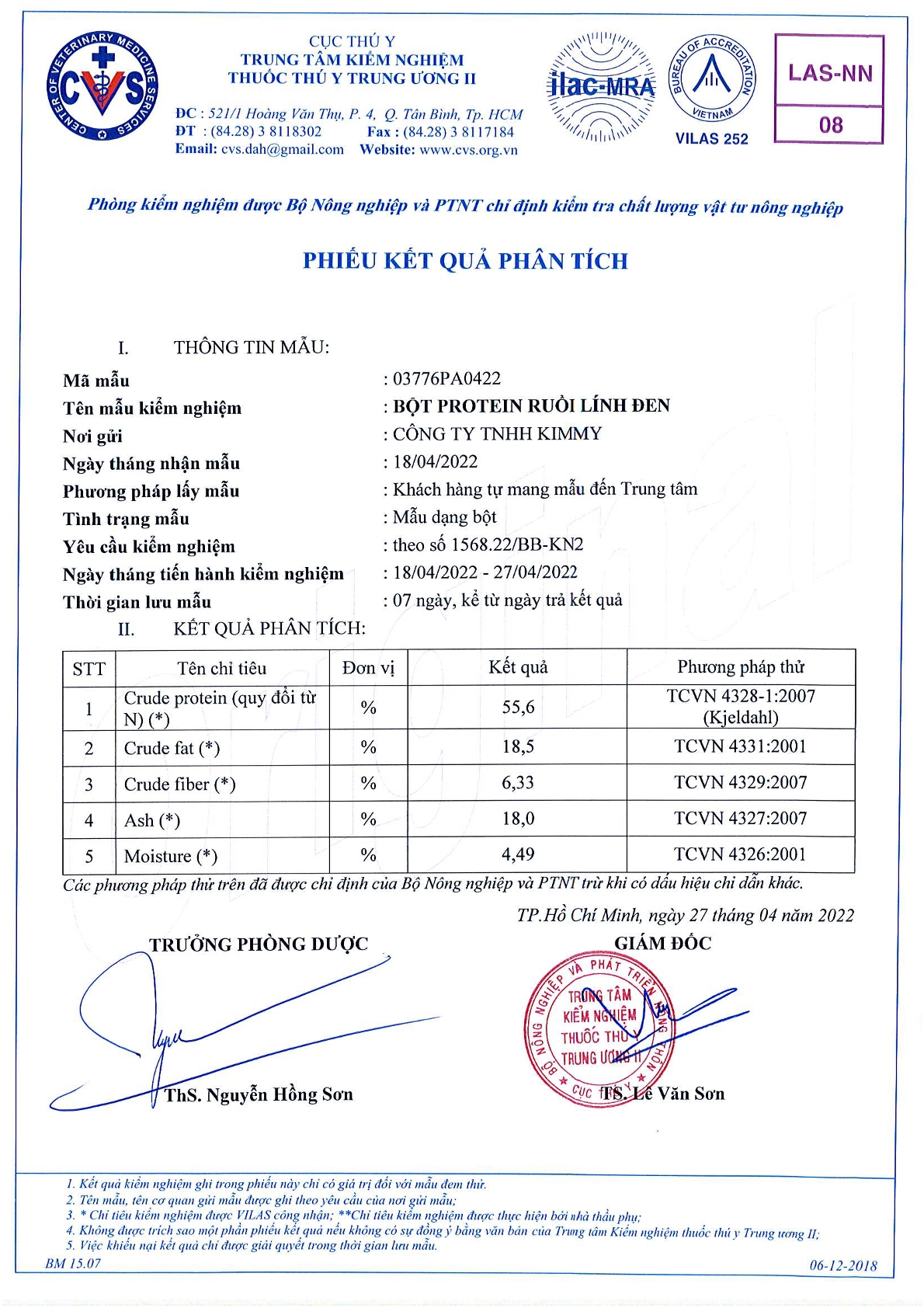
Nutritional Profile of Black Soldier Fly Larvae
The nutritional composition of black soldier fly larvae is impressive, making them a highly valuable source of protein and essential nutrients. Black soldier fly larvae are rich in protein, containing up to 42 – 50% crude protein by dry weight. In addition to protein, they are also abundant in essential amino acids, healthy fats, and various vitamins and minerals. This nutrient-dense profile makes them a highly suitable and sustainable alternative to traditional protein sources such as soy and fishmeal. Notably, black soldier fly larvae are also an excellent source of calcium and lauric acid, which have numerous health benefits for animals and potentially for humans as well.
A summary of the basic Nutritional Value in BSF larvae nutrition facts 100g BSF larvae:
| NUTRIENT | % Nutritional Value – 100g Dried BSF Larvae |
|---|---|
| Protein | 50% |
| Fat | 35% |
| Calcium | 6% |
| Phosphorus | 1,2% |
| Magnesium | 1% |
| Sodium | 0,3% |
@More Info About Our Vietnam BSF Farm: CLICK HERE!
Is the Black Soldier Fly Larvae the Protein of the Future?
YES! Absolutely, the Black Soldier Fly Larvae has the potential to be the protein of the future. Its sustainability, nutritional benefits, and versatility make it a compelling candidate for addressing global food challenges and reducing the environmental footprint.
About Consumer Attitudes Towards Insect-Based Foods
The acceptance and success of insect-based foods are heavily influenced by customer sentiments. Insect-based foods, such as those made with BSFL (black soldier fly larvae) protein, have gained popularity despite initial skepticism as people become aware of their sustainability and nutritional benefits. However, obstacles remain in the form of ingrained cultural norms and individual tastes.

About Regulatory Hurdles Insect-Based Foods
While Black Soldier Fly farming is relatively easy on a small scale, achieving large-scale production is a different challenge altogether. Ensuring consistent and substantial yields will be crucial for its adoption as a primary protein source. The food industry is highly regulated for safety and quality. The Black Soldier Fly’s use in food and animal feed requires careful consideration of regulations and standards to gain acceptance.
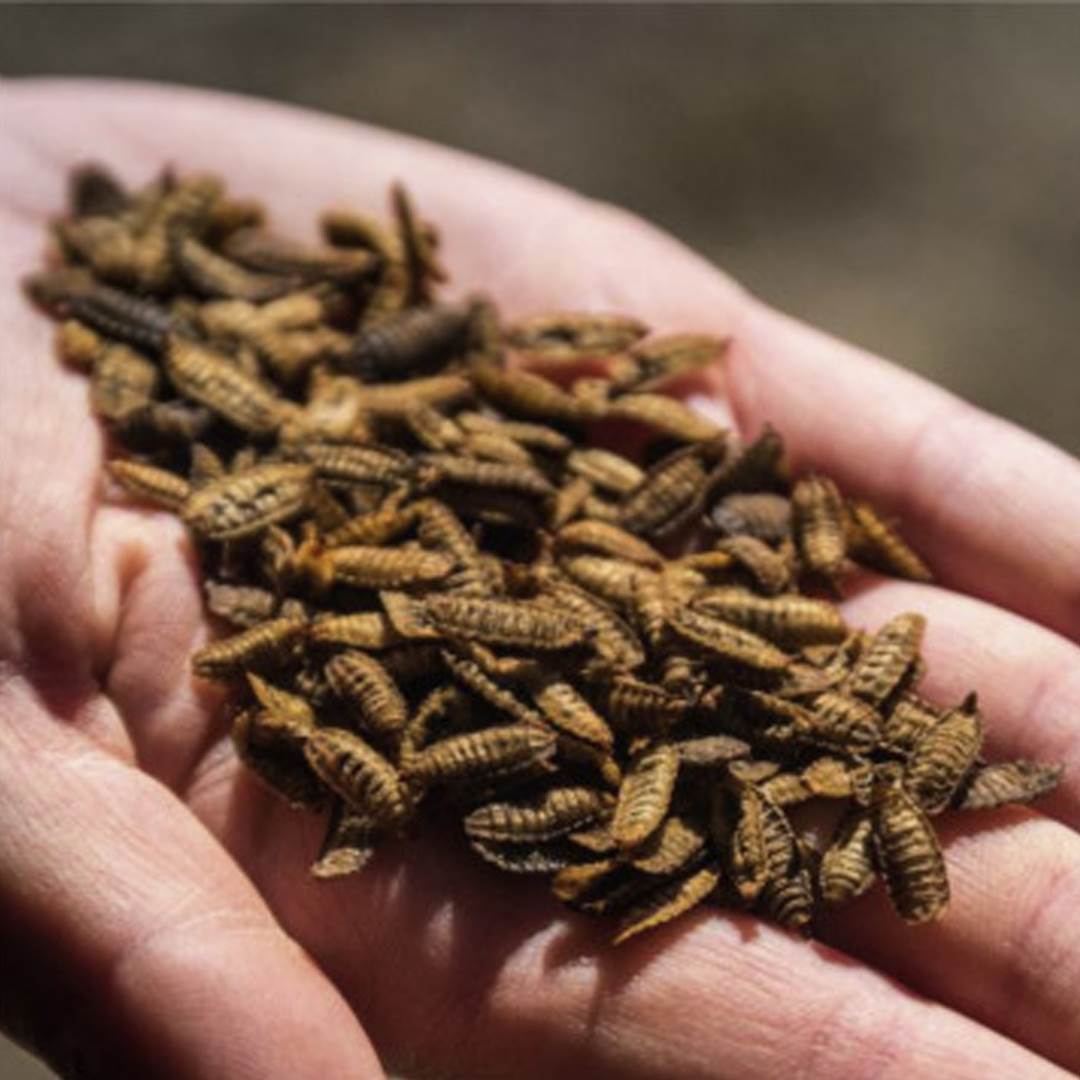

Potential Uses of Black Soldier Fly Protein in Food and Feed
The potential uses of Black Soldier Fly protein in food and feed are vast and promising. This sustainable protein source can be incorporated into a wide range of food products, including protein bars, snacks, and as a supplement in animal feed. Its high protein content, essential amino acids, and beneficial fatty acids make it a valuable ingredient for both human and animal consumption. Additionally, its potential use as a feed ingredient for aquaculture and livestock presents a solution to the increasing demand for protein while reducing reliance on traditional feed sources.


A brand specializing in the production and export of agricultural products in Vietnam. We have a black soldier fly farm in Tay Ninh and a cashew growing area in Binh Phuoc. The main export products of the company are: cashew nuts, cashew nut kernels, black soldier fly, frozen seafood, shrimp, prawns, catfish… from Vietnam.


























